
Once absorbed lithium ions substitute for sodium and potassium ions and are thought to modulate intracellular secondary messengers and potentially neurotransmitter production and release (including serotonin hence its association with serotonin toxicity).
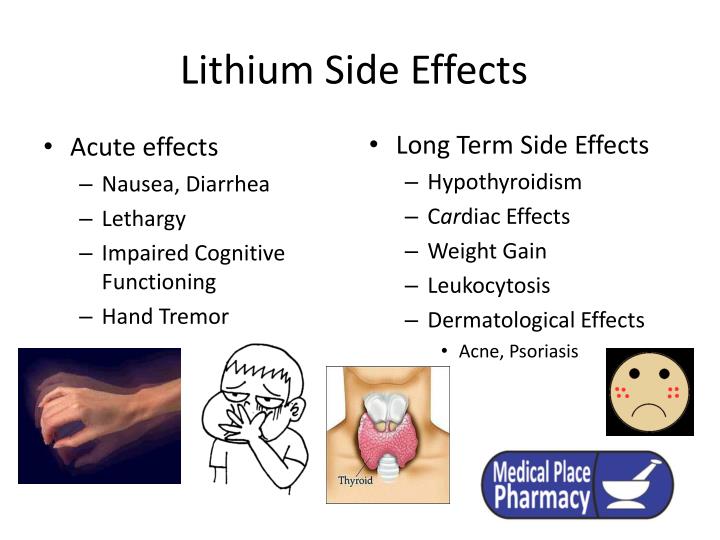
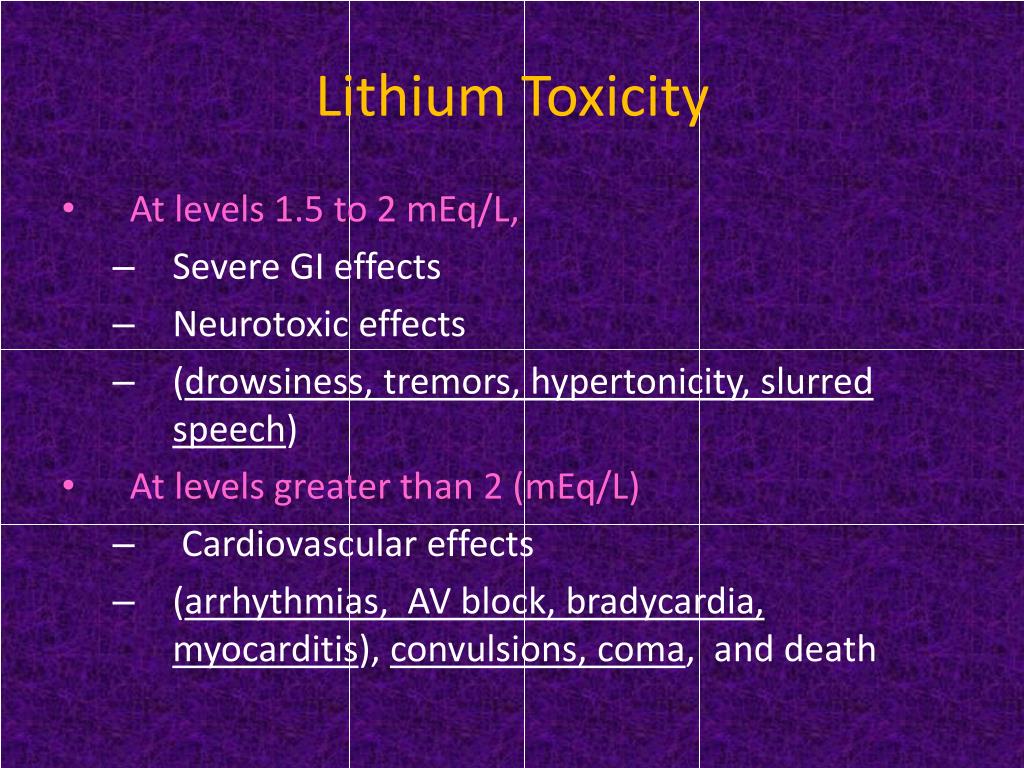
Lithium also causes a low anion gap metabolic acidosis, only two other drugs do this bromide and iodine (again an examiner’s favourite MCQ). In contrast chronic lithium toxicity has time redistribute from the gastrointestinal tract to the intravascular space and finally into the CNS resulting in neurotoxicity. Provided there is no kidney impairment neurotoxicity will not develop. Lithium is a metal and like most metals in an acute ingestion it causes nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and abdominal pain. Lithium is commonly used to treat bipolar, for your toxicology encounter it will come in two varieties, either an acute overdose or chronic toxicity and it is important to distinguish the two (examiners love this question).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
